描述
迭代器模式就是顺序访问聚集中的对象,一般来说,集合中非常常见,如果对集合类比较熟悉的话,理解本模式会十分轻松。这句话包含两层意思:一是需要遍历的对象,即聚集对象,二是迭代器对象,用于对聚集对象进行遍历访问;
注意:这里包含2个对象:
-
聚焦对象
需要遍历的对象;
-
迭代器对象
用于对聚集对象进行遍历访问的对象;
主要是对高内聚合、低耦合;
UML
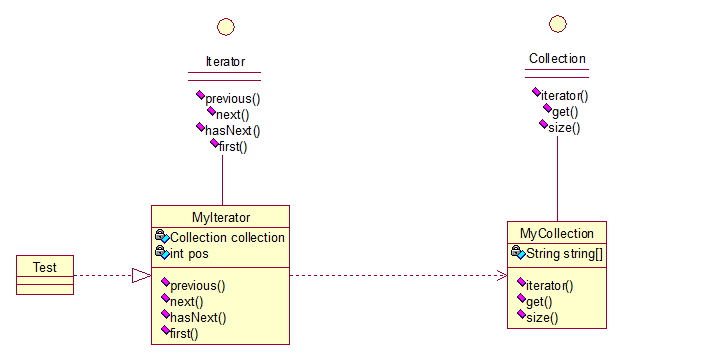
示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
|
interface Collection{
public Iterator iterator();
public Object get(int i);
public int size();
}
interface Iterator {
public Object prev();
public Object next();
public boolean hasNext();
public Object first();
}
class MyIterator implements Iterator{
private Collection collection;
private int pos=-1;
public MyIterator(Collection collection){
this.collection = collection;
}
@Override
public Object prev(){
if(pos>0){
pos--;
}
return collection.get(pos);
}
@Override
public Object next() {
if(pos<collection.size()-1){
pos++;
}
return collection.get(pos);
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if(pos<collection.size()-1){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
@Override
public Object first() {
pos = 0;
return collection.get(pos);
}
}
class MyCollection implements Collection {
public String string[] = {"a","b","c"};
@Override
public Iterator iterator(){
return new MyIterator(this);
}
@Override
public Object get(int i){
return string[i];
}
@Override
public int size(){
return string.length;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void printMsg(String msg){
System.out.println(msg);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Collection collection = new MyCollection();
Iterator it = collection.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Test.printMsg(String.valueOf(it.next()));
}
}
}
|

