适用
一般主要应用在OOP开发中的编译器的开发中,所以适用面比较窄
UML
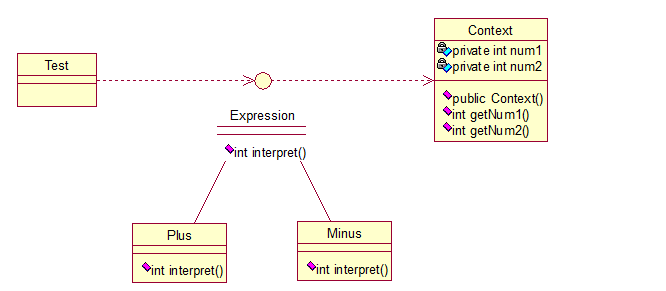
示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
class Context {
private int num1;
private int num2;
public Context(int num1, int num2) {
this.num1 = num1;
this.num2 = num2;
}
public int getNum1() {
return num1;
}
public void setNum1(int num1) {
this.num1 = num1;
}
public int getNum2() {
return num2;
}
public void setNum2(int num2) {
this.num2 = num2;
}
}
interface Expression{
public int interpret(Context context);
}
class Plus implements Expression {
@Override
public int interpret(Context context) {
return context.getNum1()+context.getNum2();
}
}
class Minus implements Expression {
@Override
public int interpret(Context context) {
return context.getNum1()-context.getNum2();
}
}
public class Test {
public static void printMsg(String msg){
System.out.println(msg);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
int result = new Minus().interpret((new Context(new Plus().interpret(new Context(9, 2)), 8)));
Test.printMsg(String.valueOf(result));
}
}
|

